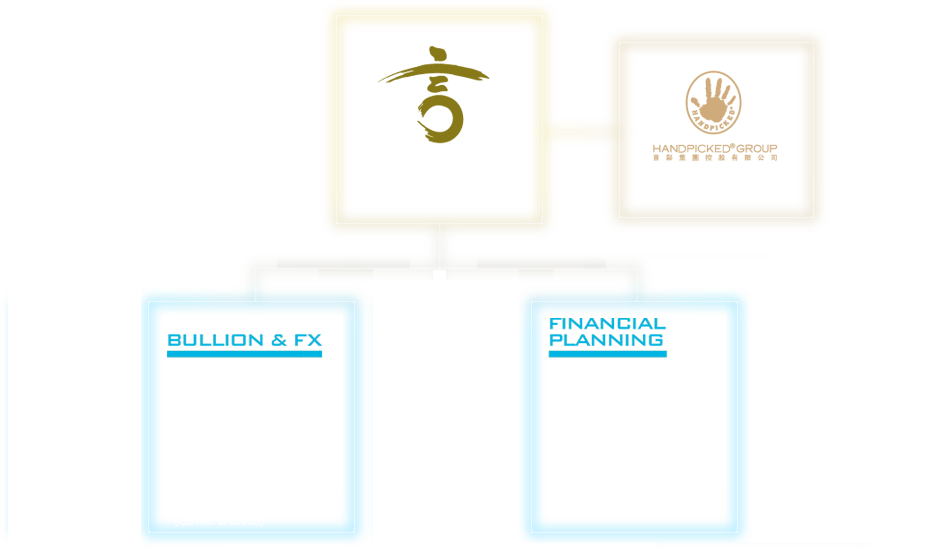
Forex Trading
KOG Forex offers leveraged foreign exchange trading including spot, options and other FX contracts. Our professional investment consultants provide customers with quotes and detailed global market information, assist in analyzing the latest market trends, so as to seize the golden opportunity for maximizing returns. Through our 24-hour online trading platform, customers can trade anytime anywhere simply with a click.
To make easy for customer to obtain the latest quotes anytime and cater for this ever-changing market, the company offers a multi-functional smartphone trading app, which provides customers not only with real-time quotes, trend charts and account management, but also a customized option strategy through specifying the underlying asset, strike price, expiry date as well as notional amount. Customers can shorten the trading time by simply using the app's ‘one-click deal’ function to confirm their transactions after getting the real-time options quotes.
What is Spot Contract? 
FOREX – BASIC CONCEPTS
Forex/
FX is a commonly used abbreviation for "foreign exchange". It
typically describes trading in the foreign exchange market, especially by
investors and speculators. "Buy Low and Sell High" means purchasing
currencies that are undervalued and selling currencies that are overvalued;
just as stock trader purchases stock that is undervalued and sells stock that
is overvalued. Customer can buy a currency pair if its exchange rate will rise
and to sell a currency pair if its exchange rate will fall.
A
currency's value fluctuates as its supply and demand fluctuates.
· An increase in supply or a decrease in demand for a currency can cause the value of that currency to fall.
· A decrease in the supply or an increase in demand for a currency can cause the value of that currency to rise.
A
big benefit to forex trading is that the customer can buy or sell any currency
pair, at any time subject to available liquidity. So if the customer believes
that the Eurozone is going to break apart, the customer can sell euro and buy
dollar (sell EUR/USD).
GO LONG OR SHORT
Unlike
the equity market, there are no limitations on short selling in the forex
currency market, no matter which way the market is moving. If the customer
believes that a currency will go up, he or she can buy it. If the customer
believes that a currency will fall, he or she can sell it. This means there is
no such thing as a bear market in forex, and the customer can make (or lose)
money any time.
LEVERAGE AND MARGIN
At HPI, leverage of 20:1 allows customers to trade with
$1,000 in the market by setting aside only $50 as a security deposit. All
trades are executed using borrowed money. This allows customers to take
advantage of leverage. This means that a customer can take advantage of even
the smallest movements in currencies by controlling more money in the market
than the customer has in the account. On the other hand, leverage can
significantly increase losses. Trading foreign exchange with any level of
leverage may not be suitable for all investors.
The specific amount that the customer is required to put aside to hold a
position is referred to as margin requirement. Margin can be thought of as a
good faith deposit required to maintain open positions. This is not a fee or a
transaction cost, it is simply a portion of the account equity set aside and
allocated as a margin deposit. In case the price movement of the
underlying asset goes against expectation, customer may be required to pay up
additional deposit.
RISK OF TRADING SPOT
Customer can
set 'limit orders' and 'stop loss orders'. A limit order places restrictions on
the maximum price to be paid or the minimum price to be received. A stop loss
order sets a particular position to be automatically liquidated at a
predetermined price. Both limit potential losses. However, customers should be
in mind that placing contingent orders, such as "stop-loss" order
will not necessarily avoid loss. Market conditions may make it impossible to
execute such orders.
What is Option Contract? 
OPTIONS – BASIC CONCEPTS
An
option is a contract giving the customer the right to acquire (i.e. buy) or dispose
(i.e. sell) an underlying asset at an agreed price before or when the contract
expires. Underlying asset refers to the asset to be acquired or disposed if the
option is exercised. The relevant asset of a foreign exchange option is the
pair of currencies the customer chooses. By utilizing different types of
options strategies, the customer will be able to seize every opportunity for
investment or hedging in the ever-changing market.
A
buyer of an option contract will pay a premium for the right to acquire or dispose
the underlying asset. On the other hand, A seller of an option contract will receive
a premium from the buyer, and will have the obligation to acquire or dispose
the underlying asset to the buyer.
HPI
acts as principal. Customer can tailor contracts with us to acquire or dispose
over-the counter options.
KEY TERMS IN OPTION TRADING
Before
understanding more about the mechanics of options trading, it is important for the
customer to know the following key terms in an option contract:
· Strike price: The pre-determined price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
· Expiry date: The last day on which a buyer of an option contract can exercise the right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
· Exercise style: It refers to when an option can be exercised. There are two exercise styles: American and European. The American-style option can be exercised during any trading day on or before the expiry date. The European-style option can only be exercised on the expiry date. HPI offers European-style option.
· Contract size: The amount of the underlying asset that an option contract represents.
· Settlement method: It refers to how the acquire/dispose of the underlying asset will be settled when the option is exercised. There are two ways of settlement - either by physical delivery of the underlying asset or in cash.
TYPES OF OPTIONS
There
are two types of options - call vs put
Call option: A call option gives the
buyer the right to acquire the underlying asset. The buyer of a call option can
determine whether to exercise the right when the market price of the underlying
asset is higher than the exercise price.
Put option: A put option gives the
buyer the right to dispose the underlying asset. The buyer of a put option can
determine whether to exercise the right when the market price of the underlying
asset is lower than the exercise price.
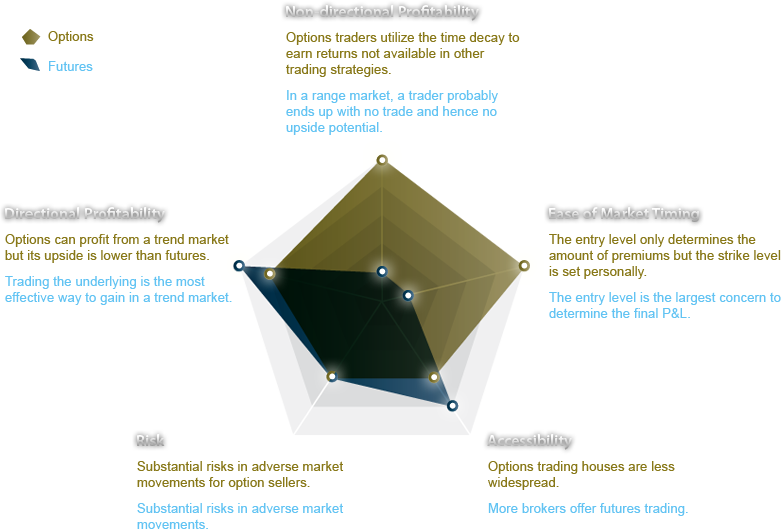
OPTIONS ≠ FUTURES
It
is a common misunderstanding to believe that options are the same as futures
because of their similarity in Chinese pronunciations (options as qi-quan 期權
and futures as qi-huo 期貨). In fact, the two are both primitive
forms of financial innovations which sequentially gained popularity in the last
century. Their greatest similarity is that they are both agreements to trade a
certain underlying asset at a future date/time (as implied by the Chinese names
both starting with qi 期).
LEVERAGE AND MARGIN
A leverage of 20:1 allows customers to trade with
$1,000 in the market by setting aside only $50 as a security deposit. All
trades are executed using borrowed money. This allows customers to take
advantage of leverage. This means that a customer can take advantage of even
the smallest movements in currencies by controlling more money in the market
than the customer has in the account. On the other hand, leverage can
significantly increase losses. Trading with any level of
leverage may not be suitable for all investors.
The specific amount that the customer is required to put aside to hold a
position is referred to as margin requirement. Margin can be thought of as a
good faith deposit required to maintain open positions. This is not a fee or a
transaction cost, it is simply a portion of the account equity set aside and
allocated as a margin deposit. In case the price movement of the
underlying asset goes against expectation, customer may be required to pay up
additional deposit.